The Kappa Architecture for Online Machine Learning
The evolution of the Lambada architecture into Kappa for Analytics and Online Machine Learning
First, a hybrid approach called the lambda architecture was introduced. This approach involves having a batch layer, a speed (stream) layer, and a serving layer. The lambda architecture provides a good balance between speed and reliability. However, the complexity introduced by having both batch and streaming pipelines can make such an architecture hard to maintain, migrate or reorganise . Due to the evolution of distributed big data systems such as Apache Kafka and Apache Spark that benefit from increased fault tolerance and availability, a new approach that removes the batch layer emerged: the kappa architecture.
These architectures are suitable for processing streaming data coming from various sources such as web analytics, sensors, application and access logs, etc. Additionally, OLTP databases can also be transformed into a data stream by replaying the operations of the database. This approach is known as Change Data Capture (CDC) and the products implementing it usually rely on monitoring the binary log of the DBMS. This stream of DB changes enables the development of more powerful real-time BI and audit use cases but it introduces data integrity concerns and configuration complexity which are usually solved in products implementing CDC. By using this unified approach, all data sources can be considered a stream and the same methods, tools, and algorithms can be used for various use cases.
Kappa Architecture for Analytics
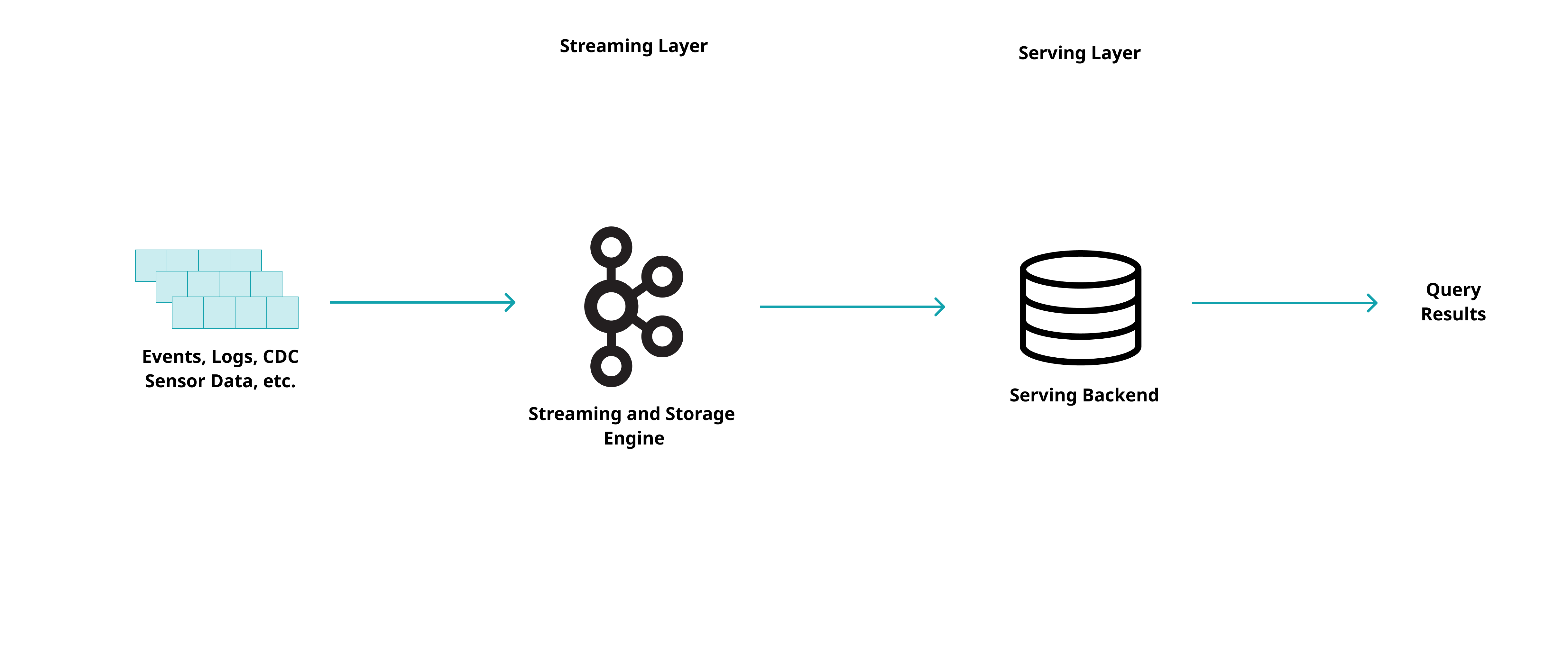
Kappa Architecture for Online Machine Learning
